The hydrogen-based direct reduction process combined with an electric arc furnace (EAF) is a known solution for the industry, but this combination is not going to solve the decarbonization challenge. The reason for this is the demand of high-quality iron ore. EAF cannot tolerate the high slag volumes that are generated in the processing of DRI from blast furnace grade iron ore. It has been estimated that currently only 4% of global iron ore supply meets the requirements of the H2-DRI +EAF steel making route. Therefore, demand and price of high-quality iron ore will increase dramatically in the future.
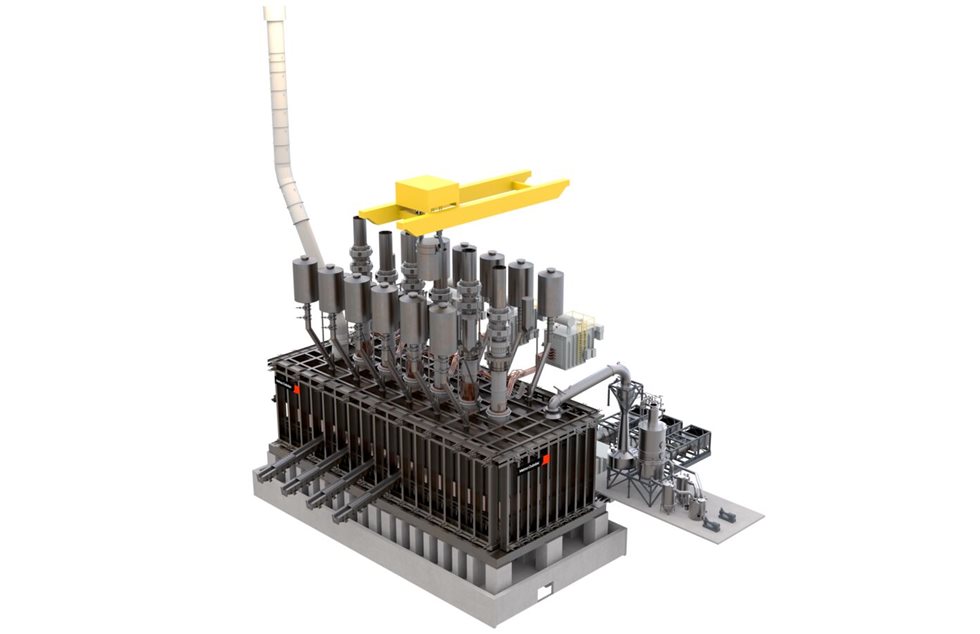
As about 71% of the existing blast furnace capacity will reach the end of its operational (relining) life before 2030, new reliable steel making processes are needed already today, if not tomorrow. Therefore, we have launched the new DRI Smelting Furnace.
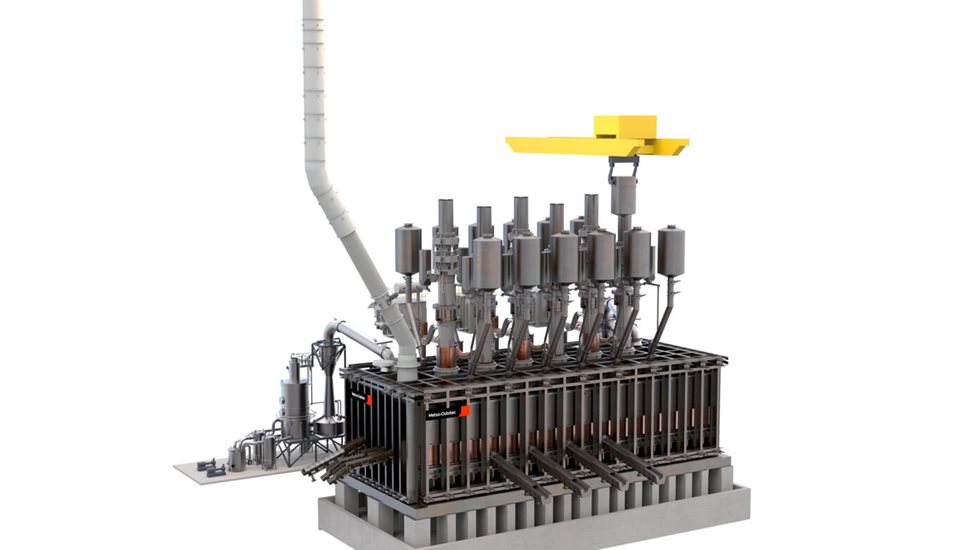
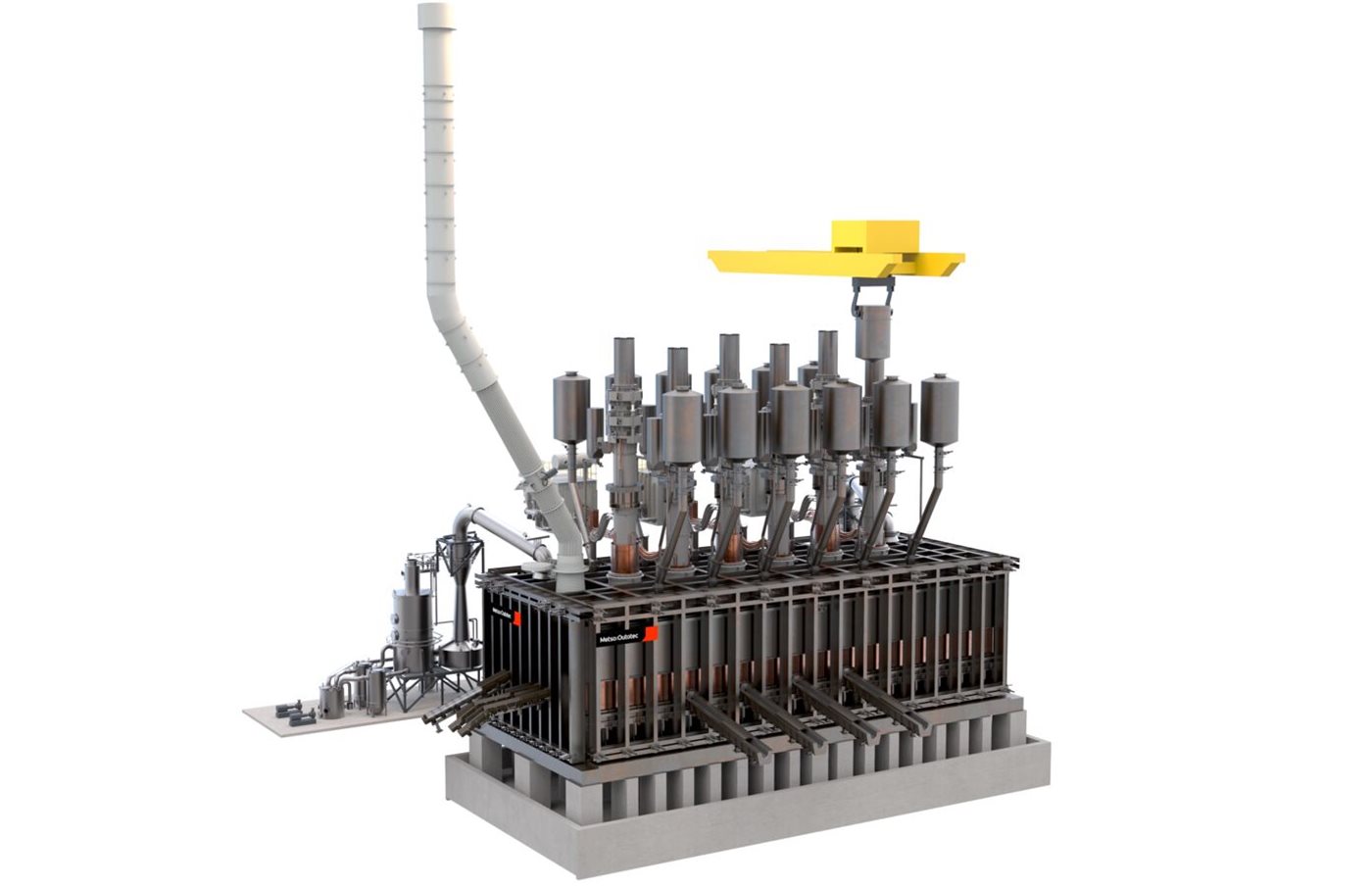
The Metso Outotec DRI Smelting Furnace can handle large slag volumes without excess iron losses, thereby allowing the use of blast furnace grade iron ore. It is a continuously operating process securing high production volumes in the steel plant. By combining direct reduction plant with our DRI Smelting Furnace and feeding DRI hot from a direct reduction plant directly into a smelting furnace, the energy efficiency of the process route can be further improved.