Supporting your operations, from plant design expertise to equipment, parts and services for every stage of your process.
Are you looking to increase production, reduce risks, lower operating costs and enhance environmental performance? Then you are in the right place.
From the design and supply of products for a greenfield plant, to the addition of a single machine for an existing production line, we are here to help.
Rely on OEM experts because not all parts are created equal. Spare and wear parts built to perform.
Helping you get the most out of your equipment and processes.


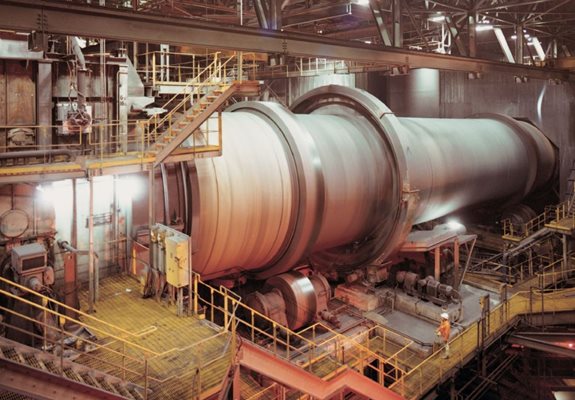
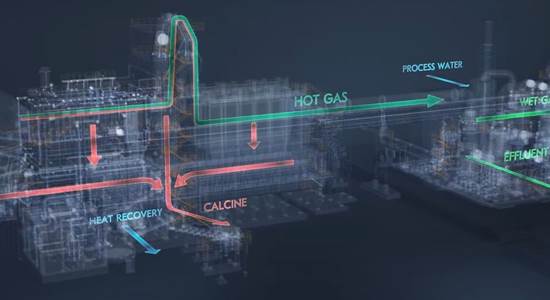
Grate Kiln systems consist of three major pieces of equipment. The Grate, the Kiln and the Cooler. The object of the process is to transform the pelletized concentrate into hardened pellets that can be used as blast furnace feed or direct reduction furnace feed.
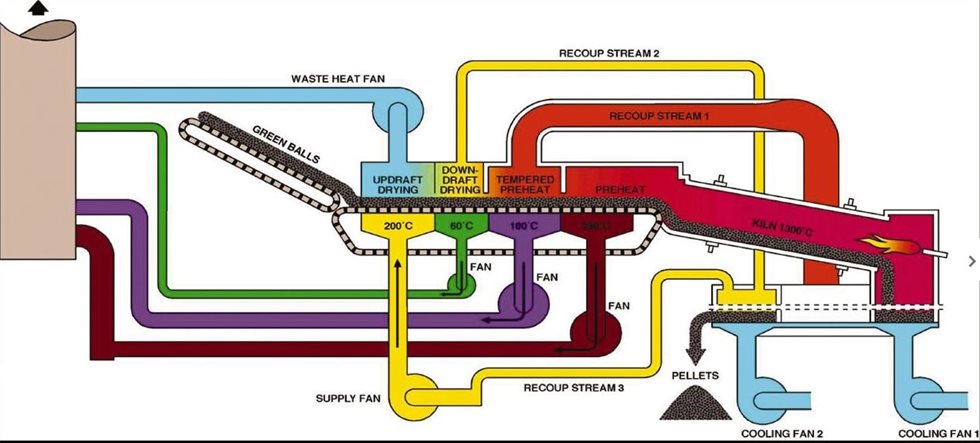
The Travelling Grate is where pellets are dried and then heated up to a temperature of about 800-900 deg C. The heat used to dry and preheat the pellets is typically hot air pulled from the Kiln and cooler. The recycling of the the hot air from the different zones increases energy efficiencies.
In the Kiln, pellets are brought up to final indurating temps. Rotation of kiln exposes entire pellet bed to heat radiating from the burner resulting in uniform pellet quality. The kiln burner utilizes cooler off gas to heat material bed to nominal of 1200-1340 °C completing the slag bonding and mineral bridging to form pellets.
In the Cooler, pellets are brought down to a suitable temperature for downstream material handling equipment. The gases from the cooler are recycled to the kiln and the grate, resulting in the Grate-Kiln being the most energy efficient system for producing indurated pellets.
Traveling grate
The traveling grate is comprised of a blanket of plates connected into a chain that carries the pellets similar to a conveyor. The difference is that the plates in the grate chain have holes in them that allows air to pass through it. The grate chain travels flat and straight. The grate travels through a furnace with several zones that expose the pellets to different temperatures. Once the pellets are discharged into the kiln, the grate chain returns underneath. The grate is driven by a motor with gearbox or hydraulic drive. The grate is supported by rollers.
Rotary kiln
The final induration of the pellet is accomplished in a rotary kiln, wherein the principal heat transfer mechanism is radiation from the system's main burner.
The process system is designed so that material transfer from the grate to the kiln occurs when the material on the grate is sufficiently preheated to have the requisite indurate strength for subsequent processing in the rotary kiln.
A rotary kiln is a steel round shell with refractory lining that rotates. This shell is rotated by a drive gear and electric or hydraulic drive system. The shell is supported on large bearings. There is a single large burner that heats the pellets up as they travel through the kiln.
Annular cooler
An annular cooler is a turntable that holds the hot pellets. Ambient air is blown through the hot pellets. The turntable is made of wedge shaped pans. The pellets fall out of the kiln directly onto the pans. The pellets travel all around the turntable until the pan is tipped and the pellets fall underneath. The pan is then righted to accept more material. The cooler pans are supported by rollers.